983 lines
56 KiB
Markdown
983 lines
56 KiB
Markdown
# 课程安排
|
||
- 物流信息的需求分析
|
||
- 技术实现分析
|
||
- 基于MongoDB的功能实现
|
||
- 多级缓存的解决方案
|
||
- Redis缓存存在的问题分析并解决
|
||
# 1、背景说明
|
||
快递员将包裹取走之后,直至收件人签收,期间发件人和收件人最为关心的就是“快递到哪了”,如何让收发件人清晰的了解到包裹的“实时”状态,就需要将物流信息给用户展现出来,也就是今天要学习的主要内容【物流信息】。
|
||
然而,此功能的并发量是有一定要求的,特别是在电商大促期间,快件数量非常庞大,也就意味着查询人的量也是很大的,所以,此处必须是缓存应用的集中地,我们也将在该业务中讲解Redis缓存应用的常见问题,并且去实施解决,从而形成通用的解决方案。
|
||
如果这块搞不好,程序员又要背锅了……
|
||

|
||
# 2、需求分析
|
||
用户寄件后,是需要查看运单的运输详情,也就是需要查看整个转运节点,类似这样:
|
||

|
||
产品的需求描述如下(在快递员端的产品文档中):
|
||

|
||
可以看出,物流信息中有状态、时间、具体信息、快递员姓名、快递员联系方式等信息。
|
||
# 3、实现分析
|
||
基于上面的需求分析,我们该如何实现呢?首先要分析一下物流信息功能的特点:
|
||
|
||
- 数据量大
|
||
- 查询频率高(签收后查询频率低)
|
||
|
||
针对于以上的特点,我们可以进行逐一的分析,首选是数据量大,这个挑战是在存储方面,如果我们做技术选型的话,无非就是两种选择,一种是关系型数据库,另一种是非关系型数据库,显然,在存储大数据方面非关系型数据库更合适一些,以我们目前掌握的技术而言,选择MongoDB存储要比MySQL更合适一些。
|
||
运单在签收之前,查询的频率是非常高的,用户可能会不断的刷物流信息,一般解决查询并发高的解决方案是通过缓存解决,我们也将对查询数据进行缓存。
|
||
## 3.1、MySQL实现
|
||
如果采用MySQL的存储,一般是这样存储的,首选设计表结构:
|
||
```sql
|
||
CREATE TABLE `sl_transport_info` (
|
||
`id` bigint NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
|
||
`transport_order_id` varchar(20) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '运单号',
|
||
`status` varchar(10) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '状态,例如:运输中',
|
||
`info` varchar(500) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '详细信息,例如:您的快件已到达【北京通州分拣中心】',
|
||
`created` datetime DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '创建时间',
|
||
`updated` datetime DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '更新时间',
|
||
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
|
||
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=8 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci;
|
||
```
|
||
插入测试数据:
|
||
```sql
|
||
INSERT INTO `sl_transport_info`(`id`, `transport_order_id`, `status`, `info`, `created`, `updated`) VALUES (1, 'SL920733749248', '已取件', '神领快递员已取件, 取件人【快递员,电话 18810966207}】', '2022-09-25 10:48:30', '2022-09-25 10:48:33');
|
||
INSERT INTO `sl_transport_info`(`id`, `transport_order_id`, `status`, `info`, `created`, `updated`) VALUES (2, 'SL920733749262', '已取件', '神领快递员已取件, 取件人【快递员,电话 18810966207}】', '2022-09-25 10:51:11', '2022-09-25 10:51:14');
|
||
INSERT INTO `sl_transport_info`(`id`, `transport_order_id`, `status`, `info`, `created`, `updated`) VALUES (3, 'SL920733749248', '运输中', '您的快件已到达【昌平区转运中心】', '2022-09-25 11:14:33', '2022-09-25 11:14:36');
|
||
INSERT INTO `sl_transport_info`(`id`, `transport_order_id`, `status`, `info`, `created`, `updated`) VALUES (4, 'SL920733749248', '运输中', '您的快件已到达【北京市转运中心】', '2022-09-25 11:14:54', '2022-09-25 11:14:57');
|
||
INSERT INTO `sl_transport_info`(`id`, `transport_order_id`, `status`, `info`, `created`, `updated`) VALUES (5, 'SL920733749262', '运输中', '您的快件已到达【昌平区转运中心】', '2022-09-25 11:15:17', '2022-09-25 11:15:19');
|
||
INSERT INTO `sl_transport_info`(`id`, `transport_order_id`, `status`, `info`, `created`, `updated`) VALUES (6, 'SL920733749262', '运输中', '您的快件已到达【江苏省南京市玄武区长江路】', '2022-09-25 11:15:44', '2022-09-25 11:15:47');
|
||
INSERT INTO `sl_transport_info`(`id`, `transport_order_id`, `status`, `info`, `created`, `updated`) VALUES (7, 'SL920733749248', '已签收', '您的快递已签收,如有疑问请联系快递员【快递员},电话18810966207】,感谢您使用神领快递,期待再次为您服务', '2022-09-25 11:16:16', '2022-09-25 11:16:19');
|
||
```
|
||

|
||
查询运单号【SL920733749248】的物流信息:
|
||
```sql
|
||
SELECT
|
||
*
|
||
FROM
|
||
sl_transport_info
|
||
WHERE
|
||
transport_order_id = 'SL920733749248'
|
||
ORDER BY
|
||
created ASC
|
||
```
|
||
结果:
|
||

|
||
## 3.2、MongoDB实现
|
||
基于MongoDB的实现,可以充分利用MongoDB数据结构的特点,可以这样存储:
|
||
```json
|
||
{
|
||
"_id": ObjectId("62c6c679a1222549d64ba01e"),
|
||
"transportOrderId": "SL1000000000585",
|
||
"infoList": [
|
||
{
|
||
"created": NumberLong("1657192271195"),
|
||
"info": "神领快递员已取件, 取件人【快递员,电话 18810966207}】",
|
||
"status": "已取件"
|
||
},
|
||
{
|
||
"created": NumberLong("1657192328518"),
|
||
"info": "神领快递员已取件, 取件人【快递员,电话 18810966207}】",
|
||
"status": "已取件"
|
||
}
|
||
],
|
||
"created": NumberLong("1657194104987"),
|
||
"updated": NumberLong("1657194105064"),
|
||
"_class": "com.sl.transport.info.entity.TransportInfoEntity"
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
如果有新的信息加入的话,只需要向【infoList】中插入元素即可,查询的话按照【transportOrderId】条件查询。
|
||
`db.sl_transport_info.find({"transportOrderId":"SL1000000000585"})`
|
||

|
||
## 3.3、分析
|
||
从上面的实现分析来看,MySQL存储在一张表中,每条物流信息就是一条行数据,数据条数将是运单数量的数倍,查询时需要通过运单id作为条件,按照时间正序排序得到所有的结果,而MongoDB存储基于其自身特点可以将物流信息列表存储到属性中,数据量等于运单量,查询时只需要按照运单id查询即可。
|
||
所以,使用MongoDB存储更适合物流信息这样的场景,我们将基于MongoDB进行实现。
|
||
# 4、功能实现
|
||
## 4.1、Service实现
|
||
在TransportInfoService中定义了3个方法:
|
||
|
||
- `saveOrUpdate()` 新增或更新数据
|
||
- `queryByTransportOrderId()` 根据运单号查询物流信息
|
||
### 4.2.1、saveOrUpdate
|
||
```java
|
||
@Resource
|
||
private MongoTemplate mongoTemplate;
|
||
|
||
@Override
|
||
public TransportInfoEntity saveOrUpdate(String transportOrderId, TransportInfoDetail infoDetail) {
|
||
//根据运单id查询
|
||
Query query = Query.query(Criteria.where("transportOrderId").is(transportOrderId)); //构造查询条件
|
||
TransportInfoEntity transportInfoEntity = this.mongoTemplate.findOne(query, TransportInfoEntity.class);
|
||
if (ObjectUtil.isEmpty(transportInfoEntity)) {
|
||
//运单信息不存在,新增数据
|
||
transportInfoEntity = new TransportInfoEntity();
|
||
transportInfoEntity.setTransportOrderId(transportOrderId);
|
||
transportInfoEntity.setInfoList(ListUtil.toList(infoDetail));
|
||
transportInfoEntity.setCreated(System.currentTimeMillis());
|
||
} else {
|
||
//运单信息存在,只需要追加物流详情数据
|
||
transportInfoEntity.getInfoList().add(infoDetail);
|
||
}
|
||
//无论新增还是更新都要设置更新时间
|
||
transportInfoEntity.setUpdated(System.currentTimeMillis());
|
||
|
||
//保存/更新到MongoDB
|
||
return this.mongoTemplate.save(transportInfoEntity);
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
### 4.2.2、查询
|
||
根据运单号查询物流信息。
|
||
```java
|
||
@Override
|
||
public TransportInfoEntity queryByTransportOrderId(String transportOrderId) {
|
||
//定义查询条件
|
||
Query query = Query.query(Criteria.where("transportOrderId").is(transportOrderId));
|
||
//查询数据
|
||
return this.mongoTemplate.findOne(query, TransportInfoEntity.class);
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
### 4.2.3、测试
|
||
通过测试用例进行测试:
|
||
```java
|
||
package com.sl.transport.info.service;
|
||
|
||
import com.sl.transport.info.entity.TransportInfoDetail;
|
||
import com.sl.transport.info.entity.TransportInfoEntity;
|
||
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
|
||
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
|
||
|
||
import javax.annotation.Resource;
|
||
|
||
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
|
||
|
||
@SpringBootTest
|
||
class TransportInfoServiceTest {
|
||
|
||
@Resource
|
||
private TransportInfoService transportInfoService;
|
||
|
||
@Test
|
||
void saveOrUpdate() {
|
||
String transportOrderId = "SL1000000001561";
|
||
TransportInfoDetail transportInfoDetail = TransportInfoDetail.builder()
|
||
.status("已取件")
|
||
.info("神领快递员已取件,取件人【张三】,电话:13888888888")
|
||
.created(System.currentTimeMillis())
|
||
.build();
|
||
TransportInfoEntity transportInfoEntity = this.transportInfoService.saveOrUpdate(transportOrderId, transportInfoDetail);
|
||
System.out.println(transportInfoEntity);
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
@Test
|
||
void queryByTransportOrderId() {
|
||
String transportOrderId = "SL1000000001561";
|
||
this.transportInfoService.queryByTransportOrderId(transportOrderId);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
测试结果:
|
||

|
||
## 4.2、记录物流信息
|
||
### 4.2.1、分析
|
||
通过前面的需求分析,可以发现新增物流信息的节点比较多,在取件、派件、物流转运环节都有记录物流信息,站在整体架构的方面的考虑,该如何在众多的业务点钟记录物流信息呢?
|
||
一般而言,会有两种方式,一种是微服务直接调用,另一种是通过消息的方式调用,也就是同步和异步的方式。选择哪种方式比较好呢?
|
||
在这里,我们选择通过消息的方式,主要原因有两个:
|
||
|
||
- 物流信息数据的更新的实时性并不高,例如,运单到达某个转运中心,晚几分种记录信息也是可以的。
|
||
- 更新数据时,并发量比较大,例如,一辆车装了几千或几万个包裹,到达某个转运中心后,司机入库时,需要一下记录几千或几万个运单的物流数据,在这一时刻并发量是比较大的,通过消息的方式,可以进行对流量削峰,从而保障系统的稳定性。
|
||
### 4.2.2、消息结构
|
||
消息的结构如下:
|
||
```json
|
||
{
|
||
"info": "您的快件已到达【$organId】",
|
||
"status": "运输中",
|
||
"organId": 1012479939628238305,
|
||
"transportOrderId": "SL920733749248",
|
||
"created": 1653133234913
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
可以看出,在消息中,有具体信息、状态、机构id、运单号、时间,其中在info字段中,约定通过`$organId`占位符表示机构,也就是,需要通过传入的`organId`查询机构名称替换到`info`中,当然了,如果没有机构,无需替换。
|
||
### 4.2.3、功能实现
|
||
在TransportInfoMQListener中对消息进行处理。
|
||
```java
|
||
package com.sl.transport.info.mq;
|
||
|
||
import cn.hutool.core.convert.Convert;
|
||
import cn.hutool.core.util.StrUtil;
|
||
import cn.hutool.json.JSONUtil;
|
||
import com.sl.ms.transport.api.OrganFeign;
|
||
import com.sl.transport.common.constant.Constants;
|
||
import com.sl.transport.common.vo.TransportInfoMsg;
|
||
import com.sl.transport.domain.OrganDTO;
|
||
import com.sl.transport.info.entity.TransportInfoDetail;
|
||
import com.sl.transport.info.service.TransportInfoService;
|
||
import org.springframework.amqp.core.ExchangeTypes;
|
||
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Exchange;
|
||
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Queue;
|
||
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.QueueBinding;
|
||
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
|
||
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
|
||
|
||
import javax.annotation.Resource;
|
||
|
||
/**
|
||
* 物流信息消息
|
||
*/
|
||
@Component
|
||
public class TransportInfoMQListener {
|
||
|
||
@Resource
|
||
private OrganFeign organFeign;
|
||
@Resource
|
||
private TransportInfoService transportInfoService;
|
||
|
||
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
|
||
value = @Queue(name = Constants.MQ.Queues.TRANSPORT_INFO_APPEND),
|
||
exchange = @Exchange(name = Constants.MQ.Exchanges.TRANSPORT_INFO, type = ExchangeTypes.TOPIC),
|
||
key = Constants.MQ.RoutingKeys.TRANSPORT_INFO_APPEND
|
||
))
|
||
public void listenTransportInfoMsg(String msg) {
|
||
//{"info":"您的快件已到达【$organId】", "status":"运输中", "organId":90001, "transportOrderId":920733749248 , "created":1653133234913}
|
||
TransportInfoMsg transportInfoMsg = JSONUtil.toBean(msg, TransportInfoMsg.class);
|
||
Long organId = transportInfoMsg.getOrganId();
|
||
String transportOrderId = Convert.toStr(transportInfoMsg.getTransportOrderId());
|
||
String info = transportInfoMsg.getInfo();
|
||
|
||
//查询机构信息
|
||
if (StrUtil.contains(info, "$organId")) {
|
||
OrganDTO organDTO = this.organFeign.queryById(organId);
|
||
if (organDTO == null) {
|
||
return;
|
||
}
|
||
info = StrUtil.replace(info, "$organId", organDTO.getName());
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
//封装Detail对象
|
||
TransportInfoDetail infoDetail = TransportInfoDetail.builder()
|
||
.info(info)
|
||
.status(transportInfoMsg.getStatus())
|
||
.created(transportInfoMsg.getCreated()).build();
|
||
|
||
//存储到MongoDB
|
||
this.transportInfoService.saveOrUpdate(transportOrderId, infoDetail);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
### 4.2.4、测试
|
||
此次测试通过发消息的方式进行,可以在RabbitMQ的管理界面中今天发送消息:
|
||

|
||

|
||
结果:
|
||

|
||
# 5、多级缓存解决方案
|
||
目前我们已经实现了物流信息的保存、更新操作,基本功能已经了ok了,但是有个问题我们还没解决,就是前面提到的并发大的问题,一般而言,解决查询并发大的问题,常见的手段是为查询接口增加缓存,从而可以减轻持久层的压力。
|
||
按照我们以往的经验,在查询接口中增加Redis缓存即可,将查询的结果数据存储到Redis中,执行查询时首先从Redis中命中,如果命中直接返回即可,没有命中查询MongoDB,将解决写入到Redis中。
|
||
这样就解决问题了吗?其实并不是,试想一下,如果Redis宕机了或者是Redis中的数据大范围的失效,这样大量的并发压力就会进入持久层,会对持久层有较大的影响,甚至可能直接崩溃。
|
||
如何解决该问题呢,可以通过多级缓存的解决方案来进行解决。
|
||
## 5.1、什么是多级缓存
|
||

|
||
由上图可以看出,在用户的一次请求中,可以设置多个缓存以提升查询的性能,能够快速响应。
|
||
|
||
- 浏览器的本地缓存
|
||
- 使用Nginx作为反向代理的架构时,可以启用Nginx的本地缓存,对于代理数据进行缓存
|
||
- 如果Nginx的本地缓存未命中,可以在Nginx中编写Lua脚本从Redis中命中数据
|
||
- 如果Redis依然没有命中的话,请求就会进入到Tomcat,也就是执行我们写的程序,在程序中可以设置进程级的缓存,如果命中直接返回即可。
|
||
- 如果进程级的缓存依然没有命中的话,请求才会进入到持久层查询数据。
|
||
|
||
以上就是多级缓存的基本的设计思路,其核心思想就是让每一个请求节点尽可能的进行缓存操作。
|
||
:::danger
|
||
🚨说明,由于我们没有学习过Lua脚本,所以我们将Redis的查询逻辑放到程序中进行,也就是我们将要在程序中实现二级缓存,分别是:JVM进程缓存和Redis缓存。
|
||
:::
|
||
## 5.2、Caffeine快速入门
|
||
Caffeine是一个基于Java8开发的,提供了近乎最佳命中率的高性能的本地缓存库,也就是可以通过Caffeine实现进程级的缓存。Spring内部的缓存使用的就是Caffeine。
|
||
Caffeine的性能非常强悍,下图是官方给出的性能对比:
|
||

|
||
### 5.2.1、使用
|
||
导入依赖:
|
||
```xml
|
||
<!--jvm进程缓存-->
|
||
<dependency>
|
||
<groupId>com.github.ben-manes.caffeine</groupId>
|
||
<artifactId>caffeine</artifactId>
|
||
</dependency>
|
||
```
|
||
基本使用:
|
||
```java
|
||
package com.sl.transport.info.service;
|
||
|
||
import com.github.benmanes.caffeine.cache.Cache;
|
||
import com.github.benmanes.caffeine.cache.Caffeine;
|
||
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
|
||
|
||
public class CaffeineTest {
|
||
|
||
@Test
|
||
public void testCaffeine() {
|
||
// 创建缓存对象
|
||
Cache<String, Object> cache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
|
||
.initialCapacity(10) //缓存初始容量
|
||
.maximumSize(100) //缓存最大容量
|
||
.build();
|
||
|
||
//将数据存储缓存中
|
||
cache.put("key1", 123);
|
||
|
||
// 从缓存中命中数据
|
||
// 参数一:缓存的key
|
||
// 参数二:Lambda表达式,表达式参数就是缓存的key,方法体是在未命中时执行
|
||
// 优先根据key查询进程缓存,如果未命中,则执行参数二的Lambda表达式,执行完成后会将结果写入到缓存中
|
||
Object value1 = cache.get("key1", key -> 456);
|
||
System.out.println(value1); //123
|
||
|
||
Object value2 = cache.get("key2", key -> 456);
|
||
System.out.println(value2); //456
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
### 5.2.2、驱逐策略
|
||
Caffeine既然是缓存的一种,肯定需要有缓存的清除策略,不然的话内存总会有耗尽的时候。
|
||
Caffeine提供了三种缓存驱逐策略:
|
||
|
||
- **基于容量**:设置缓存的数量上限
|
||
```java
|
||
// 创建缓存对象
|
||
Cache<String, String> cache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
|
||
.maximumSize(1) // 设置缓存大小上限为 1,当缓存超出这个容量的时候,会使用Window TinyLfu策略来删除缓存。
|
||
.build();
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
- **基于时间**:设置缓存的有效时间
|
||
```java
|
||
// 创建缓存对象
|
||
Cache<String, String> cache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
|
||
// 设置缓存有效期为 10 秒,从最后一次写入开始计时
|
||
.expireAfterWrite(Duration.ofSeconds(10))
|
||
.build();
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
- **基于引用**:设置缓存为软引用或弱引用,利用GC来回收缓存数据。性能较差,不建议使用。
|
||
:::danger
|
||
**🚨注意:**在默认情况下,当一个缓存元素过期的时候,Caffeine不会自动立即将其清理和驱逐。而是在一次读或写操作后,或者在空闲时间完成对失效数据的驱逐。
|
||
:::
|
||
## 5.3、一级缓存
|
||
下面我们通过增加Caffeine实现一级缓存,主要是在 `com.sl.transport.info.controller.TransportInfoController` 中实现缓存逻辑。
|
||
### 5.3.1、Caffeine配置
|
||
```java
|
||
package com.sl.transport.info.config;
|
||
|
||
import com.github.benmanes.caffeine.cache.Cache;
|
||
import com.github.benmanes.caffeine.cache.Caffeine;
|
||
import com.sl.transport.info.domain.TransportInfoDTO;
|
||
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
|
||
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
|
||
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
|
||
|
||
/**
|
||
* Caffeine缓存配置
|
||
*/
|
||
@Configuration
|
||
public class CaffeineConfig {
|
||
|
||
@Value("${caffeine.init}")
|
||
private Integer init;
|
||
@Value("${caffeine.max}")
|
||
private Integer max;
|
||
|
||
@Bean
|
||
public Cache<String, TransportInfoDTO> transportInfoCache() {
|
||
return Caffeine.newBuilder()
|
||
.initialCapacity(init)
|
||
.maximumSize(max).build();
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
具体的配置项在Nacos中的配置中心的`sl-express-ms-transport-info.properties`中:
|
||

|
||
### 5.3.2、实现缓存逻辑
|
||
在`com.sl.transport.info.controller.TransportInfoController`中进行数据的命中,如果命中直接返回,没有命中查询MongoDB。
|
||
```java
|
||
/**
|
||
* 根据运单id查询运单信息
|
||
*
|
||
* @param transportOrderId 运单号
|
||
* @return 运单信息
|
||
*/
|
||
@ApiImplicitParams({
|
||
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "transportOrderId", value = "运单id")
|
||
})
|
||
@ApiOperation(value = "查询", notes = "根据运单id查询物流信息")
|
||
@GetMapping("{transportOrderId}")
|
||
public TransportInfoDTO queryByTransportOrderId(@PathVariable("transportOrderId") String transportOrderId) {
|
||
TransportInfoDTO transportInfoDTO = this.transportInfoCache.get(transportOrderId, s -> {
|
||
TransportInfoEntity transportInfoEntity = this.transportInfoService.queryByTransportOrderId(transportOrderId);
|
||
return BeanUtil.toBean(transportInfoEntity, TransportInfoDTO.class);
|
||
});
|
||
|
||
if (ObjectUtil.isNotEmpty(transportInfoDTO)) {
|
||
return transportInfoDTO;
|
||
}
|
||
throw new SLException(ExceptionEnum.NOT_FOUND);
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
### 5.3.3、测试
|
||
未命中场景:
|
||

|
||
已命中:
|
||

|
||
响应结果:
|
||

|
||
## 5.4、二级缓存
|
||
二级缓存通过Redis的存储实现,这里我们使用Spring Cache进行缓存数据的存储和读取。
|
||
### 5.4.1、Redis配置
|
||
Spring Cache默认是采用jdk的对象序列化方式,这种方式比较占用空间而且性能差,所以往往会将值以json的方式存储,此时就需要对RedisCacheManager进行自定义的配置。
|
||
```java
|
||
package com.sl.transport.info.config;
|
||
|
||
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
|
||
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
|
||
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
|
||
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration;
|
||
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
|
||
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
|
||
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
|
||
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializationContext;
|
||
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
|
||
|
||
import java.time.Duration;
|
||
|
||
/**
|
||
* Redis相关的配置
|
||
*/
|
||
@Configuration
|
||
public class RedisConfig {
|
||
|
||
/**
|
||
* 存储的默认有效期时间,单位:小时
|
||
*/
|
||
@Value("${redis.ttl:1}")
|
||
private Integer redisTtl;
|
||
|
||
@Bean
|
||
public RedisCacheManager redisCacheManager(RedisTemplate redisTemplate) {
|
||
// 默认配置
|
||
RedisCacheConfiguration defaultCacheConfiguration = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
|
||
// 设置key的序列化方式为字符串
|
||
.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer()))
|
||
// 设置value的序列化方式为json格式
|
||
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer()))
|
||
.disableCachingNullValues() // 不缓存null
|
||
.entryTtl(Duration.ofHours(redisTtl)); // 默认缓存数据保存1小时
|
||
|
||
// 构redis缓存管理器
|
||
RedisCacheManager redisCacheManager = RedisCacheManager.RedisCacheManagerBuilder
|
||
.fromConnectionFactory(redisTemplate.getConnectionFactory())
|
||
.cacheDefaults(defaultCacheConfiguration)
|
||
.transactionAware() // 只在事务成功提交后才会进行缓存的put/evict操作
|
||
.build();
|
||
return redisCacheManager;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
### 5.4.2、缓存注解
|
||
接下来需要在Service中增加SpringCache的注解,确保数据可以保存、更新数据到Redis。
|
||
```java
|
||
@Override
|
||
@CachePut(value = "transport-info", key = "#p0") //更新缓存数据
|
||
public TransportInfoEntity saveOrUpdate(String transportOrderId, TransportInfoDetail infoDetail) {
|
||
//省略代码
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
@Override
|
||
@Cacheable(value = "transport-info", key = "#p0") //新增缓存数据
|
||
public TransportInfoEntity queryByTransportOrderId(String transportOrderId) {
|
||
//省略代码
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
### 5.4.3、测试
|
||
重启服务,进行功能测试,发现数据可以正常写入到Redis中,并且查询时二级缓存已经生效。
|
||

|
||
到这里,已经完成了一级和二级缓存的逻辑。
|
||
## 5.5、一级缓存更新的问题
|
||
更新物流信息时,只是更新了Redis中的数据,并没有更新Caffeine中的数据,需要在更新数据时将Caffeine中相应的数据删除。
|
||
具体实现如下:
|
||
```java
|
||
@Resource
|
||
private Cache<String, TransportInfoDTO> transportInfoCache;
|
||
|
||
@Override
|
||
@CachePut(value = "transport-info", key = "#p0") //更新缓存数据
|
||
public TransportInfoEntity saveOrUpdate(String transportOrderId, TransportInfoDetail infoDetail) {
|
||
//省略代码
|
||
|
||
//清除缓存中的数据
|
||
this.transportInfoCache.invalidate(transportOrderId);
|
||
|
||
//保存/更新到MongoDB
|
||
return this.mongoTemplate.save(transportInfoEntity);
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
这样的话就可以删除Caffeine中的数据,也就意味着下次查询时会从二级缓存中查询到数据,再存储到Caffeine中。
|
||
## 5.6、分布式场景下的问题
|
||
### 5.6.1、问题分析
|
||
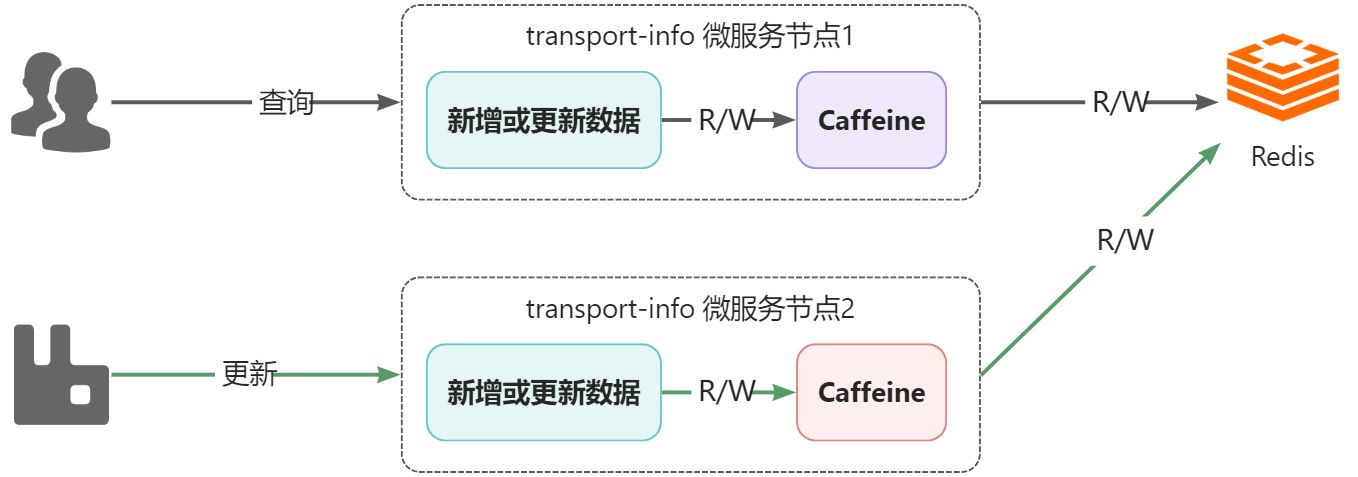
通过前面的解决,视乎可以完成一级、二级缓存中数据的同步,如果在单节点项目中是没有问题的,但是,在分布式场景下是有问题的,看下图:
|
||
|
||
说明:
|
||
|
||
- 部署了2个transport-info微服务节点,每个微服务都有自己进程级的一级缓存,都共享同一个Redis作为二级缓存
|
||
- 假设,所有节点的一级和二级缓存都是空的,此时,用户通过节点1查询运单物流信息,在完成后,节点1的caffeine和Redis中都会有数据
|
||
- 接着,系统通过节点2更新了物流数据,此时节点2中的caffeine和Redis都是更新后的数据
|
||
- 用户还是进行查询动作,依然是通过节点1查询,此时查询到的将是旧的数据,也就是出现了一级缓存与二级缓存之间的数据不一致的问题
|
||
### 5.6.2、问题解决
|
||
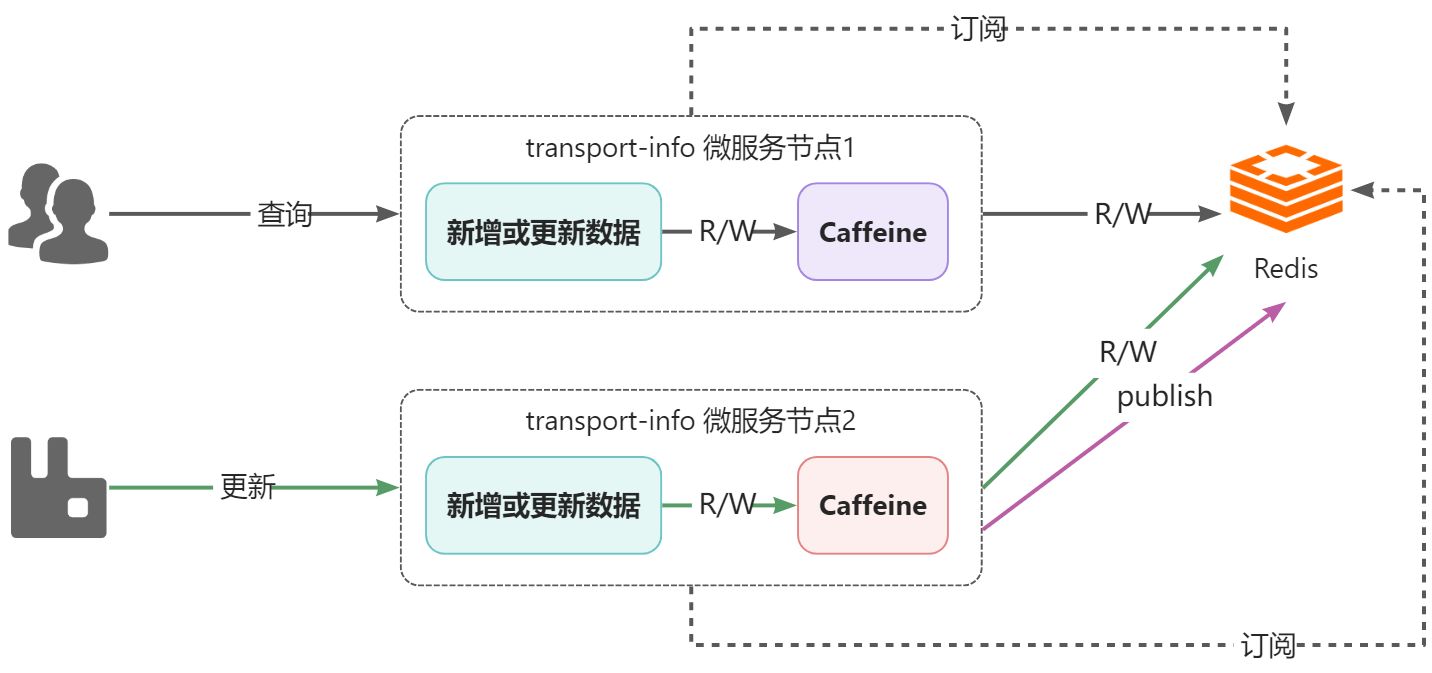
如何解决该问题呢?可以通过消息的方式解决,就是任意一个节点数据更新了数据,发个消息出来,通知其他节点,其他节点接收到消息后,将自己caffeine中相应的数据删除即可。
|
||
关于消息的实现,可以采用RabbitMQ,也可以采用Redis的消息订阅发布来实现,在这里为了应用技术的多样化,所以采用Redis的订阅发布来实现。
|
||
|
||
:::info
|
||
Redis 发布订阅(pub/sub)是一种消息通信模式:发送者(pub)发送消息,订阅者(sub)接收消息。
|
||

|
||
当有新消息通过 publish 命令发送给频道 channel1 时, 这个消息就会被发送给订阅它的三个客户端。
|
||
Redis的订阅发布功能与传统的消息中间件(如:RabbitMQ)相比,相对轻量一些,针对数据准确和安全性要求没有那么高的场景可以直接使用。
|
||
:::
|
||
在`com.sl.transport.info.config.RedisConfig`增加订阅的配置:
|
||
```java
|
||
public static final String CHANNEL_TOPIC = "sl-express-ms-transport-info-caffeine";
|
||
|
||
/**
|
||
* 配置订阅,用于解决Caffeine一致性的问题
|
||
*
|
||
* @param connectionFactory 链接工厂
|
||
* @param listenerAdapter 消息监听器
|
||
* @return 消息监听容器
|
||
*/
|
||
@Bean
|
||
public RedisMessageListenerContainer container(RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory,
|
||
MessageListenerAdapter listenerAdapter) {
|
||
RedisMessageListenerContainer container = new RedisMessageListenerContainer();
|
||
container.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);
|
||
container.addMessageListener(listenerAdapter, new ChannelTopic(CHANNEL_TOPIC));
|
||
return container;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
编写`RedisMessageListener`用于监听消息,删除caffeine中的数据。
|
||
```java
|
||
package com.sl.transport.info.mq;
|
||
|
||
import cn.hutool.core.convert.Convert;
|
||
import com.github.benmanes.caffeine.cache.Cache;
|
||
import com.sl.transport.info.domain.TransportInfoDTO;
|
||
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.Message;
|
||
import org.springframework.data.redis.listener.adapter.MessageListenerAdapter;
|
||
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
|
||
|
||
import javax.annotation.Resource;
|
||
|
||
/**
|
||
* redis消息监听,解决Caffeine一致性的问题
|
||
*/
|
||
@Component
|
||
public class RedisMessageListener extends MessageListenerAdapter {
|
||
|
||
@Resource
|
||
private Cache<String, TransportInfoDTO> transportInfoCache;
|
||
|
||
@Override
|
||
public void onMessage(Message message, byte[] pattern) {
|
||
//获取到消息中的运单id
|
||
String transportOrderId = Convert.toStr(message);
|
||
//将本jvm中的缓存删除掉
|
||
this.transportInfoCache.invalidate(transportOrderId);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
更新数据后发送消息:
|
||
```java
|
||
@Resource
|
||
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
|
||
|
||
@Override
|
||
@CachePut(value = "transport-info", key = "#p0")
|
||
public TransportInfoEntity saveOrUpdate(String transportOrderId, TransportInfoDetail infoDetail) {
|
||
//省略代码
|
||
|
||
//清除缓存中的数据
|
||
// this.transportInfoCache.invalidate(transportOrderId);
|
||
//发布订阅消息到redis
|
||
this.stringRedisTemplate.convertAndSend(RedisConfig.CHANNEL_TOPIC, transportOrderId);
|
||
|
||
//保存/更新到MongoDB
|
||
return this.mongoTemplate.save(transportInfoEntity);
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
### 5.6.3、测试
|
||
测试时,需要启动2个相同的微服务,但是端口不能重复,需要设置不同的端口:
|
||

|
||
通过测试,发现可以接收到Redis订阅的消息:
|
||

|
||
最终可以解决多级缓存间的一致性的问题。
|
||
# 6、Redis的缓存问题
|
||
在使用Redis时,在高并发场景下会出现一些问题,常见的问题有:缓存击穿、缓存雪崩、缓存穿透,这三个问题也是面试时的高频问题。
|
||
## 6.1、缓存击穿
|
||
### 6.1.1、说明
|
||
缓存击穿是指,某一热点数据存储到redis中,该数据处于高并发场景下,如果此时该key过期失效,这样就会有大量的并发请求进入到数据库,对数据库产生大的压力,甚至会压垮数据库。
|
||
### 6.1.2、解决方案
|
||
针对于缓存击穿这种情况,常见的解决方案有两种:
|
||
|
||
- 热数据不设置过期时间
|
||
- 使用互斥锁,可以使用redisson的分布式锁实现,就是从redis中查询不到数据时,不要立刻去查数据库,而是先获取锁,获取到锁后再去查询数据库,而其他未获取到锁的请求进行重试,这样就可以确保只有一个查询数据库并且更新缓存的请求。
|
||

|
||
### 6.1.3、实现
|
||
在物流信息场景中,不涉及到此类问题,一般用户只会关注自己的运单信息,而不是并发的查询一个运单信息,所以该问题我们就暂不做实现,但是此类问题的解决方案的思想要学会。
|
||
当然了,防止有人恶意根据运单号查询,可以通过设置验证码的方式进行,如下(韵达快递官网):
|
||

|
||
## 6.2、缓存雪崩
|
||
### 6.2.1、说明
|
||
缓存雪崩的情况往往是由两种情况产生:
|
||
|
||
- 情况1:由于大量 key 设置了相同的过期时间(数据在缓存和数据库都存在),一旦到达过期时间点,这些 key 集体失效,造成访问这些 key 的请求全部进入数据库。
|
||
- 情况2:Redis 实例宕机,大量请求进入数据库
|
||
### 6.2.2、解决方案
|
||
针对于雪崩问题,可以分情况进行解决:
|
||
|
||
- 情况1的解决方案
|
||
- 错开过期时间:在过期时间上加上随机值(比如 1~5 分钟)
|
||
- 服务降级:暂停非核心数据查询缓存,返回预定义信息(错误页面,空值等)
|
||
- 情况2的解决方案
|
||
- 事前预防:搭建高可用集群
|
||
- 构建多级缓存,实现成本稍高
|
||
- 熔断:通过监控一旦雪崩出现,暂停缓存访问待实例恢复,返回预定义信息(有损方案)
|
||
- 限流:通过监控一旦发现数据库访问量超过阈值,限制访问数据库的请求数(有损方案)
|
||
### 6.2.3、实现
|
||
我们将针对【情况1】的解决方案进行实现,主要是在默认的时间基础上随机增加1-10分钟有效期时间。
|
||
需要注意的是,使用SpringCache的`@Cacheable`注解是无法指定有效时间的,所以需要自定义`RedisCacheManager`对有效期时间进行随机设置。
|
||
自定义`RedisCacheManager`:
|
||
```java
|
||
package com.sl.transport.info.config;
|
||
|
||
import cn.hutool.core.util.ObjectUtil;
|
||
import cn.hutool.core.util.RandomUtil;
|
||
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCache;
|
||
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration;
|
||
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
|
||
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheWriter;
|
||
|
||
import java.time.Duration;
|
||
|
||
/**
|
||
* 自定义CacheManager,用于设置不同的过期时间,防止雪崩问题的发生
|
||
*/
|
||
public class MyRedisCacheManager extends RedisCacheManager {
|
||
|
||
public MyRedisCacheManager(RedisCacheWriter cacheWriter, RedisCacheConfiguration defaultCacheConfiguration) {
|
||
super(cacheWriter, defaultCacheConfiguration);
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
@Override
|
||
protected RedisCache createRedisCache(String name, RedisCacheConfiguration cacheConfig) {
|
||
//获取到原有过期时间
|
||
Duration duration = cacheConfig.getTtl();
|
||
if (ObjectUtil.isNotEmpty(duration)) {
|
||
//在原有时间上随机增加1~10分钟
|
||
Duration newDuration = duration.plusMinutes(RandomUtil.randomInt(1, 11));
|
||
cacheConfig = cacheConfig.entryTtl(newDuration);
|
||
}
|
||
return super.createRedisCache(name, cacheConfig);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
使用`MyRedisCacheManager`:
|
||
```java
|
||
@Bean
|
||
public RedisCacheManager redisCacheManager(RedisTemplate redisTemplate) {
|
||
// 默认配置
|
||
RedisCacheConfiguration defaultCacheConfiguration = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
|
||
// 设置key的序列化方式为字符串
|
||
.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer()))
|
||
// 设置value的序列化方式为json格式
|
||
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer()))
|
||
.disableCachingNullValues() // 不缓存null
|
||
.entryTtl(Duration.ofHours(redisTtl)); // 默认缓存数据保存1小时
|
||
|
||
// 构redis缓存管理器
|
||
// RedisCacheManager redisCacheManager = RedisCacheManager.RedisCacheManagerBuilder
|
||
// .fromConnectionFactory(redisTemplate.getConnectionFactory())
|
||
// .cacheDefaults(defaultCacheConfiguration)
|
||
// .transactionAware()
|
||
// .build();
|
||
|
||
//使用自定义缓存管理器
|
||
RedisCacheWriter redisCacheWriter = RedisCacheWriter.nonLockingRedisCacheWriter(redisTemplate.getConnectionFactory());
|
||
MyRedisCacheManager myRedisCacheManager = new MyRedisCacheManager(redisCacheWriter, defaultCacheConfiguration);
|
||
myRedisCacheManager.setTransactionAware(true); // 只在事务成功提交后才会进行缓存的put/evict操作
|
||
return myRedisCacheManager;
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
### 6.2.4、测试
|
||

|
||

|
||
## 6.3、缓存穿透
|
||
### 6.3.1、说明
|
||
缓存穿透是指,如果一个 key 在缓存和数据库都不存在,那么访问这个 key 每次都会进入数据库
|
||
|
||
- 很可能被恶意请求利用
|
||
- 缓存雪崩与缓存击穿都是数据库中有,但缓存暂时缺失
|
||
- 缓存雪崩与缓存击穿都能自然恢复,但缓存穿透则不能
|
||
### 6.3.2、解决方案
|
||
针对缓存穿透,一般有两种解决方案,分别是:
|
||
|
||
- 如果数据库没有,也将此不存在的 key 关联 null 值放入缓存,缺点是这样的 key 没有任何业务作用,白占空间
|
||
- 采用BloomFilter(布隆过滤器)解决,基本思路就是将存在数据的哈希值存储到一个足够大的Bitmap(Bit为单位存储数据,可以大大节省存储空间)中,在查询redis时,先查询布隆过滤器,如果数据不存在直接返回即可,如果存在的话,再执行缓存中命中、数据库查询等操作。
|
||
### 6.3.3、布隆过滤器
|
||
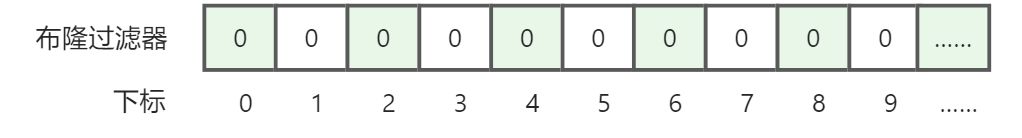
布隆过滤器(Bloom Filter)是1970年由布隆提出的,它实际上是一个很长的二进制向量和一系列随机映射函数,既然是二进制,那存储的数据不是0就是1,默认是0。
|
||
可以把它看作是这样的:
|
||
|
||
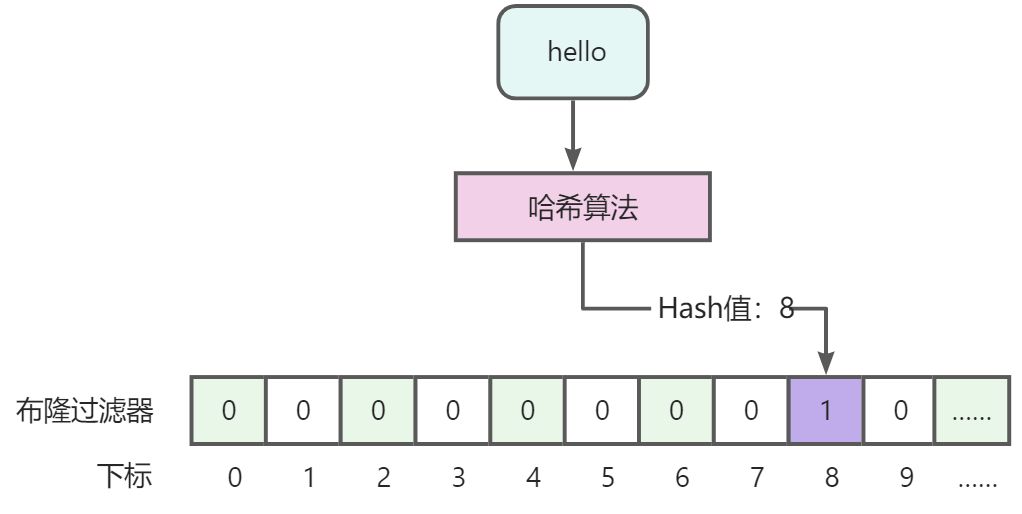
需要将数据存入隆过滤器中,才能判断是否存在,存入时要通过哈希算法计算数据的哈希值,通过哈希值确定存储都哪个位置。如下:
|
||
|
||
:::danger
|
||
说明:数据hello通过哈希算法计算哈希值,假设得到的值为8,这个值就是存储到布隆过滤器下标值。
|
||
:::
|
||
如何判断数据存在或者不存在呢?和存储道理一样,假设判断【java】数据是否存在,首先通过哈希算法计算哈希值,通过下标判断值是0还是1,如果是0就不存在,1就存在。
|
||
:::info
|
||
看到这里,你一定会有这样的疑问,不同的数据经过哈希算法计算,可能会得到相同的值,也就是,【张三】和【王五】可能会得到相同的hash值,会在同一个位置标记为1,这样的话,1个位置可能会代表多个数据,也就是会出现误判,没错,这个就是布隆过滤器最大的一个缺点,也是不可避免的特性。正因为这个特性,所以布隆过滤器基本是不能做删除动作的。
|
||
:::
|
||
这里可以得出一个结论,使用布隆过滤器能够判断一定不存在,而不能用来判断一定存在。
|
||
布隆过滤器虽然不能完全避免误判,但是可以降低误判率,如何降低误判率呢?就是增加多个哈希算法,计算多个hash值,因为不同的值,经过多个哈希算法计算得到相同值的概率要低一些。
|
||
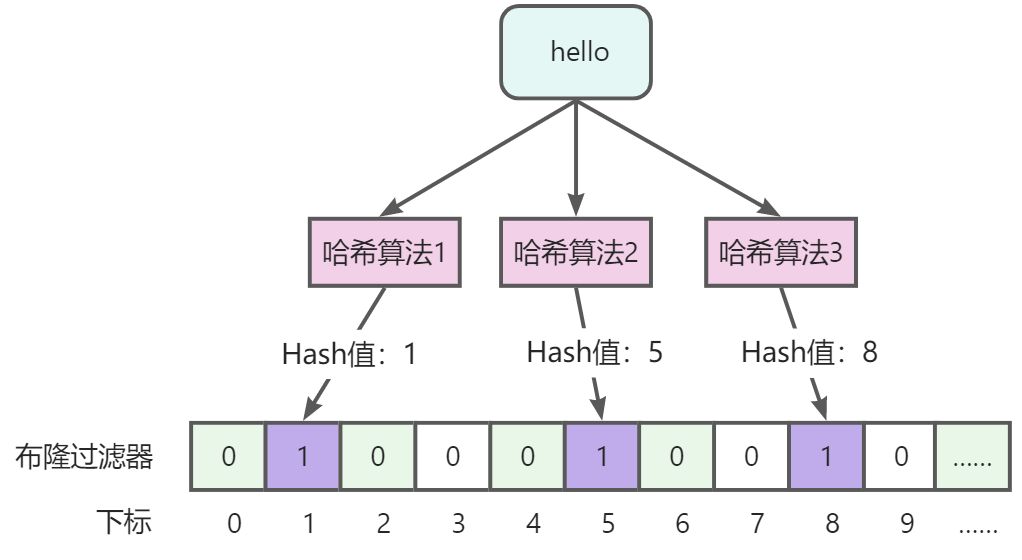
|
||
:::danger
|
||
说明:可以看到,【hello】值经过3个哈希算法(实际不止3个)会计算出3个值,分别以这些值为坐标,标记数据为1,当判断值存在时,同样要经过这3个哈希算法计算3个哈希值,对应的都为1说明数据可能存在,如果其中有一个为0,就说明数据一定不存在。
|
||
在这里也能看出布隆过滤器的另外一个特性,哈希算法越多,误判率越低,但是所占用的空间越多,查询效率将越低。
|
||
:::
|
||
总结下布隆过滤器的优缺点:
|
||
|
||
- 优点
|
||
- 存储的二进制数据,1或0,不存储真实数据,空间占用比较小且安全。
|
||
- 插入和查询速度非常快,因为是基于数组下标的,类似HashMap,其时间复杂度是O(K),其中k是指哈希算法个数。
|
||
- 缺点
|
||
- 存在误判,可以通过增加哈希算法个数降低误判率,不能完全避免误判。
|
||
- 删除困难,因为一个位置可能会代表多个值,不能做删除。
|
||
|
||
牢记结论:布隆过滤器能够判断一定不存在,而不能用来判断一定存在。
|
||
### 6.3.4、实现
|
||
关于布隆过滤器的使用,建议使用Google的Guava 或 Redission基于Redis实现,前者是在单体架构下比较适合,后者更适合在分布式场景下,便于多个服务节点之间共享。
|
||
Redission基于Redis,使用string类型数据,生成二进制数组进行存储,最大可用长度为:4294967294。
|
||
引入Redission依赖:
|
||
```xml
|
||
<dependency>
|
||
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
|
||
<artifactId>redisson</artifactId>
|
||
</dependency>
|
||
```
|
||
导入Redission的配置:
|
||
```java
|
||
package com.sl.transport.info.config;
|
||
|
||
import cn.hutool.core.convert.Convert;
|
||
import cn.hutool.core.util.StrUtil;
|
||
import org.redisson.Redisson;
|
||
import org.redisson.api.RedissonClient;
|
||
import org.redisson.config.Config;
|
||
import org.redisson.config.SingleServerConfig;
|
||
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisProperties;
|
||
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
|
||
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
|
||
|
||
import javax.annotation.Resource;
|
||
|
||
@Configuration
|
||
public class RedissonConfiguration {
|
||
|
||
@Resource
|
||
private RedisProperties redisProperties;
|
||
|
||
@Bean
|
||
public RedissonClient redissonSingle() {
|
||
Config config = new Config();
|
||
SingleServerConfig serverConfig = config.useSingleServer()
|
||
.setAddress("redis://" + redisProperties.getHost() + ":" + redisProperties.getPort());
|
||
if (null != (redisProperties.getTimeout())) {
|
||
serverConfig.setTimeout(1000 * Convert.toInt(redisProperties.getTimeout().getSeconds()));
|
||
}
|
||
if (StrUtil.isNotEmpty(redisProperties.getPassword())) {
|
||
serverConfig.setPassword(redisProperties.getPassword());
|
||
}
|
||
return Redisson.create(config);
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
自定义布隆过滤器配置:
|
||
```java
|
||
package com.sl.transport.info.config;
|
||
|
||
import lombok.Getter;
|
||
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
|
||
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
|
||
|
||
/**
|
||
* 布隆过滤器相关配置
|
||
*/
|
||
@Getter
|
||
@Configuration
|
||
public class BloomFilterConfig {
|
||
|
||
/**
|
||
* 名称,默认:sl-bloom-filter
|
||
*/
|
||
@Value("${bloom.name:sl-bloom-filter}")
|
||
private String name;
|
||
|
||
/**
|
||
* 布隆过滤器长度,最大支持Integer.MAX_VALUE*2,即:4294967294,默认:1千万
|
||
*/
|
||
@Value("${bloom.expectedInsertions:10000000}")
|
||
private long expectedInsertions;
|
||
|
||
/**
|
||
* 误判率,默认:0.05
|
||
*/
|
||
@Value("${bloom.falseProbability:0.05d}")
|
||
private double falseProbability;
|
||
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
定义`BloomFilterService`接口:
|
||
```java
|
||
package com.sl.transport.info.service;
|
||
|
||
/**
|
||
* 布隆过滤器服务
|
||
*/
|
||
public interface BloomFilterService {
|
||
|
||
/**
|
||
* 初始化布隆过滤器
|
||
*/
|
||
void init();
|
||
|
||
/**
|
||
* 向布隆过滤器中添加数据
|
||
*
|
||
* @param obj 待添加的数据
|
||
* @return 是否成功
|
||
*/
|
||
boolean add(Object obj);
|
||
|
||
/**
|
||
* 判断数据是否存在
|
||
*
|
||
* @param obj 数据
|
||
* @return 是否存在
|
||
*/
|
||
boolean contains(Object obj);
|
||
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
编写实现类:
|
||
```java
|
||
package com.sl.transport.info.service.impl;
|
||
|
||
import com.sl.transport.info.config.BloomFilterConfig;
|
||
import com.sl.transport.info.service.BloomFilterService;
|
||
import org.redisson.api.RBloomFilter;
|
||
import org.redisson.api.RedissonClient;
|
||
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
|
||
|
||
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
|
||
import javax.annotation.Resource;
|
||
|
||
@Service
|
||
public class BloomFilterServiceImpl implements BloomFilterService {
|
||
|
||
@Resource
|
||
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
|
||
@Resource
|
||
private BloomFilterConfig bloomFilterConfig;
|
||
|
||
private RBloomFilter<Object> getBloomFilter() {
|
||
return this.redissonClient.getBloomFilter(this.bloomFilterConfig.getName());
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
@Override
|
||
@PostConstruct // spring启动后进行初始化
|
||
public void init() {
|
||
RBloomFilter<Object> bloomFilter = this.getBloomFilter();
|
||
bloomFilter.tryInit(this.bloomFilterConfig.getExpectedInsertions(), this.bloomFilterConfig.getFalseProbability());
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
@Override
|
||
public boolean add(Object obj) {
|
||
return this.getBloomFilter().add(obj);
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
@Override
|
||
public boolean contains(Object obj) {
|
||
return this.getBloomFilter().contains(obj);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
改造TransportInfoController的查询逻辑,如果布隆过滤器中不存在直接返回即可,无需进行缓存命中。
|
||
```java
|
||
@ApiImplicitParams({
|
||
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "transportOrderId", value = "运单id")
|
||
})
|
||
@ApiOperation(value = "查询", notes = "根据运单id查询物流信息")
|
||
@GetMapping("{transportOrderId}")
|
||
public TransportInfoDTO queryByTransportOrderId(@PathVariable("transportOrderId") String transportOrderId) {
|
||
//如果布隆过滤器中不存在,无需缓存命中,直接返回即可
|
||
boolean contains = this.bloomFilterService.contains(transportOrderId);
|
||
if (!contains) {
|
||
throw new SLException(ExceptionEnum.NOT_FOUND);
|
||
}
|
||
TransportInfoDTO transportInfoDTO = transportInfoCache.get(transportOrderId, id -> {
|
||
//未命中,查询MongoDB
|
||
TransportInfoEntity transportInfoEntity = this.transportInfoService.queryByTransportOrderId(id);
|
||
//转化成DTO
|
||
return BeanUtil.toBean(transportInfoEntity, TransportInfoDTO.class);
|
||
});
|
||
|
||
if (ObjectUtil.isNotEmpty(transportInfoDTO)) {
|
||
return transportInfoDTO;
|
||
}
|
||
throw new SLException(ExceptionEnum.NOT_FOUND);
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
改造`com.sl.transport.info.service.impl.TransportInfoServiceImpl#saveOrUpdate()`方法,将新增的运单数据写入到布隆过滤器中:
|
||

|
||
:::danger
|
||
可见,通过布隆过滤器可以解决缓存穿透的问题,还有一点需要注意,如果有存在的数据没有写入都布隆过滤器中就会导致查询不到真实存在的数据。
|
||
:::
|
||
# 7、练习
|
||
## 7.1、练习1
|
||
难度系数:★★★★☆
|
||
描述:在work微服务中完成发送【物流信息】的消息的逻辑,这样的话,work微服务就和transport-info微服务联系起来了。
|
||
提示,一共有4处代码需要完善:
|
||
|
||
- com.sl.ms.work.mq.CourierMQListener#listenCourierPickupMsg()
|
||
- com.sl.ms.work.service.impl.PickupDispatchTaskServiceImpl#saveTaskPickupDispatch()
|
||
- 此处实现难度较大,会涉及到基础服务系统消息模块,需要阅读相应的代码进行理解。
|
||
- com.sl.ms.work.service.impl.TransportOrderServiceImpl#updateStatus()
|
||
- com.sl.ms.work.service.impl.TransportOrderServiceImpl#updateByTaskId()
|
||
:::danger
|
||
另外,包裹的签收与拒收的消息已经在【快递员微服务】中实现,学生可自行阅读源码:
|
||
|
||
- com.sl.ms.web.courier.service.impl.TaskServiceImpl#sign()
|
||
- com.sl.ms.web.courier.service.impl.TaskServiceImpl#reject()
|
||
:::
|
||
# 8、面试连环问
|
||
:::info
|
||
面试官问:
|
||
|
||
- 你们项目中的物流信息那块存储是怎么做的?为什么要选择MongoDB?
|
||
- 针对于查询并发高的问题你们是怎么解决的?有用多级缓存吗?具体是怎么用的?
|
||
- 多级缓存间的数据不一致是如何解决的?
|
||
- 来,说说在使用Redis场景中的缓存击穿、缓存雪崩、缓存穿透都是啥意思?对应的解决方案是啥?实际你解决过哪个问题?
|
||
- 说说布隆过滤器的优缺点是什么?什么样的场景适合使用布隆过滤器?
|
||
:::
|